This territory is the birthplace of the Chabad guru, rabbi Menachem Mendel Schneerson, of the first mayor of Tel-Aviv and ofKlezmer music. Also a good home to Trotsky, for a while.
It was meant to be a second Palestine, but Stalin ruined their plans.
And the only gentile I know that got this far with his research on this topic was murdered.
ABSTRACT
PREAMBLE
- Zelensky is controlled by Chabad.
- Putin is controlled by Chabad.
- Chabad doesn’t argue itself.
- Chabad doesn’t find a peace resolution in Ukraine.
_______________________________________
Conclusion: The resolution is war.
Which would explain why Russia doesn’t seem to hurry or throw its best resources into this pit.
If Chabad wins either way, who loses either way?
The local population, the dead ones especially. The ones in the separatist regions and the South most specifically, as they’re the only Ukrainians shelled by Ukrainian Army rather than by the “invaders”.
But the ripples are global and can be manipulated in more ways than we can imagine.
Doesn’t that victimized local population include lots of Chabad / Jews?
Not quite, they’re mostly gone by now, but promise to return, as this Kharkov Chabad rabbi announced on April 22, 2022:
Who are the Jews of Ukraine, according to Chabad.org :
“Today, Ukraine boasts a thriving Jewish infrastructure that includes synagogues, mikvahs, a matzah bakery, Jewish schools and yeshivahs, and social services organizations. The first permanent post-Perestroika Chabad-Lubavitch emissaries to Ukraine arrived in 1990 to what was still the Soviet Union, and began leading the synagogues in Kharkov and Dnipro (Dnepropetrovsk until 2014) that had just been returned to the Jewish community by the authorities. Their work built on Chabad’s deep roots in the region, including decades of underground Jewish activism throughout the Soviet era.
…
Chabad maintains Jewish orphanages in Zhitomir—the children were evacuated farther west this week—Odessa, and Dnipro. It is far from only relief work that they are engaged in. As the quality of life in Ukraine has risen, so has the quality of Jewish life. Chabad maintains a Jewish university in Odessa and has built the largest Jewish center in the world in Dnipro. Kosher restaurants dot the country as well, signaling a level of material and spiritual comfort few could have predicted just a few decades ago.
…
According to the United States Holocaust Memorial Musuem, prior to Hitler’s invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941, “Ukraine was home to the largest Jewish population in Europe… While scholars are still researching the scale of the Holocaust in Ukraine, they estimate at least one and a half million Jews were killed there.” The Nazis, with the help of local collaborators, gathered Ukraine’s Jews in local ghettos, but, for the most part, instead of deporting them to camps, shot them in forests and fields close to home. Such killing fields dot the entire Ukraine, with places such as Babi Yar outside of Kiev—where some 40,000 Jews were murdered—among the most well-known.
Many surviving Jews returned home after the war, and traces of the former Pale of Settlement were readily visible as late as the 1980s and early 90s. Back then, small, historically Jewish towns in western Ukraine still had synagogues and significant numbers of native Yiddish speakers, their concentration diminishing the farther east one went. When Chabad of Zhitomir was established in the early 1990s by Rabbi Shlomo and Esther Wilhelm, one of their responsibilities was to reach out to the dozens of smaller Jewish towns where throngs of older Jews still lived.” – Chabad.org
What I pictured so far suggests an ethnically targeted depopulation agenda and a revenge agenda that don’t argue, just may overlap with other agendas. A reverse pogrom.
Depop policies are not entirely new to them, Ukraine has hardly survived through Holodomor once, under the helms of Jews…
“Last July, the Ukrainian Security Service released a list of high-ranking Soviet state and Communist Party officials — as well as officials from NKVD, the police force of Soviet Russia — that essentially blamed Jews and Latvians responsible for perpetrating and executing the famine because most of the names on the list were Jewish.”
JEWISH TELEPGRAPHIC AGENCY, JUNE 15, 2009
“Zelensky told reporters that he had asked Netanyahu to recognize as a genocide the 1932 Holodomor famine caused by Soviet policies, but Netanyahu did not.”
JEWISH TELEPGRAPHIC AGENCY, AUG 20, 2019
But why just those specific areas, what do they have in common?
Well, it seems the disputed territory map largely overlaps with a former area of high Jewish interest:

Rare documents and press reports tell a rare story.
A CRAZY HIDDEN STORY OF ROTHSCHILD-WARBURG PROTO-COMMUNISM

| THE LIFE STORY OF SHMUEL YELISHEVITCH Related orally in Yiddish by Shmuel Yelishevitch in 1992, at the age of 92. This written record was translated simultaneously from Yiddish and written in Hebrew.[Translated by Chaim Freedman, 1998/9] I was born in a Jewish house, father, mother and seven children. I was the youngest of the six sons and the daughter who was the firstborn. We lived in an old house on an estate called Azarevitch. The estate had a Russian landowner and we worked his land. When we built a larger house, my grandfather and grandmother continued to live in the old house. Grandfather was a religious Jew and attended the synagogue every day which was one kilometer from the house. One day, a severe winter day, on the way home from the synagogue he fell and broke his foot. Due to his inability to work he wanted to move to his son Gotlieb who lived close to the synagogue. Grandmother was afraid to sleep alone in the house at night. She paid me two kopecks per night so that I should stay with her. I was then aged six and grandmother told me each evening about the history of the family which is engraved in my memory. The Colonies The estate was founded in 1800 before which it was desolate. Rothschild, who was friendly with Queen Katerina was aware of the difficult life of the Jews in Polotsk and in Vitebsk and it was forbidden for them to live in the villages unless they were craftsmen. In the same period army service in Russia was by those who were abducted whose service was for twenty five years. Rothschild approached the Queen Katerina and suggested to her to grant the Jews an area of land and he would finance the settlement of Jews there. The idea found favor with the queen, she visited the Ukraine, passed through the steppes and discovered that it was desolate and uncultivated. She suggested to Rothschild to accompany her and visit the area and it was decided to establish Jewish colonies in that area. She promulgated an order to divide the area such that each family would receive a plot of land and that those families who settled there would not be enlisted in the army. That is how they established seventeen settlements of one to two hundred families each. The largest colony was called Bakher3. Others were called Latent4, Engels, Myadler, Peness, Di Vilner, Kabilni, Gravskoy, these were on one side.On the other side there were, amongst them, Horkes, Nazrivka ( in Yiddish Azeritch where I was born), Priud, Kavalevsk, Haloshkas, Pervi (2) numer, Dritten (3) numer, Numer (4) Ferten numer, Hopalover. In between an area of sixty kilometers there were also Russian villages. Every family received forty kilometers of land, a two-family house and next to it for each family, a dunam of land to grow household needs. Two thousand dunams was left in reserve for family expansion. |

Felix Warburg Expresses Satisfaction with Jewish Settlements in Crimea
JTA, May 19, 1927
The inspection tour of the new Jewish colonies made by Felix M. Warburg and his party came to a close today with a visit to the Julius Rosenwahl Colony.
Of the 136 new Jewish colonies, 27 were visited by, Mr Warburg, who was accompanied by James II. Becker, Dr. Bernard Kahn and Dr. Joseph A. Rosen, head of the Agro-joint in Russia. In addresses to the settlers, Mr. Warburg expressed his pleasure at the rate of development and at the energy and efficiency of the colonists and the management of the Agro-joint, the agency of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee responsible for the colonization work.
What a fantastic year for mr. Felix!

And these two had more brothers, one of them, called Max, was dealing i the same money and people trafficking business “niche”:
“Together with his brother Felix M. Warburg, who was a successful banker in the U.S., Max M. Warburg organized financial aid for Jews in Eastern Europe. As the war led to increasing antisemitism, Warburg started to ask officials to protect Jews against discrimination. During the war Warburg came to be one of the leading figures to advise German politicians, diplomats, and the military in financial matters. In October 1918 he was appointed a financial advisor to the chancellor (Reichskanzler) Prinz Max von Baden. In 1919, Warburg served the German delegates during the negotiations on the Versailles peace treaty as an economic specialist. Warburg preferred to keep a low profile. When Walther *Rathenau asked him in early 1922 to join the cabinet (Reichsregierung) as minister of finance he refused, saying that two Jewish ministers would be too much for Germany. After the assassination of Rathenau the murderers planned also to kill Warburg. In 1924 he was appointed a member of the board (Generalrat) of the Reichsbank. The Warburg Bank was still one of the most important banking companies in Germany. From the late 1920s on Warburg intensified his interest in Zionism.
From World War I on, his brothers Felix M. and Paul M. Warburg opened the doors to the leading financial circles in North America for their brother. This was – again – especially helpful, when Germany urgently needed fresh capital during the world economic crisis between 1930 and 1932. After the Nazis came to power in Germany, the Warburg Bank came under increasing pressure. Max M. Warburg focused on helping Jewish emigrants to get their money out of Germany via the Palaestina-Treuhand GmbH. After the Warburg Bank was closed by the National Socialists, Warburg himself immigrated in 1938 to New York, where he died.”
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
M.M. Warburg, Aus meinen Erinnerungen (1952, edited by Eric M. Warburg); E. Rosenbaum et al., Das Bankhaus M.M. Warburg & Co. 1798 bis 1938 (1976); R. Chernow, The Warburgs (1993).
Sources: Encyclopaedia Judaica.

If this is how they treated their home-country, Germany, how much can you hope from them for America and the Federal Reserve?
Or Ukraine…

WARBURG FEDERAL RESERVE
Previously on SILVIEW.media: “THE QUESTION IS ONLY WHETHER WORLD GOVERNMENT WILL BE ACHIEVED BY CONSENT OR BY CONQUEST” – WARBURG / ROTHSCHILD PROGENITURE IN 1950 US SENATE HEARINGS
AND MR. FED REPORTED TO…
On December 15, 1931, Chairman McFadden informed the House of a dispatch in the Public Ledger of Philadelphia, October 24, 1931, “GERMAN REVEALS HOOVER’S SECRET. The American President was in intimate negotiations with the German government regarding a year’s debt holiday as early as December, 1930.” McFadden continued,
“Behind the Hoover announcement there were many months of hurried and furtive preparations both in Germany and in Wall Street offices of German bankers. Germany, like a sponge, had to be saturated with American money. Mr. Hoover himself had to be elected, because this scheme began before he became President. If the German international bankers of Wall Street — that is Kuhn Loeb Company, J. & W. Seligman, Paul Warburg, J. Henry Schroder — and their satellites had not had this job waiting to be done, Herbert Hoover would never have been elected President of the United States.
The election of Mr. Hoover to the Presidency was through the influence of the Warburg Brothers, directors of the great bank of Kuhn Loeb Company, who carried the cost of his election. In exchange for this collaboration Mr. Hoover promised to impose the moratorium of German debts. Hoover sought to exempt Kreuger’s loan to Germany of $125 million from the operation of the Hoover Moratorium. The nature of Kreuger’s swindle was known here in January when he visited his friend, Mr. Hoover, in the White House.”
Eustace Mullins – Secrets of the Federal Reserve London Connection
From Wikipedia:
Kuhn, Loeb & Co. was an American multinational investment bank founded in 1867 by Abraham Kuhn and his brother-in-law Solomon Loeb.[1] Under the leadership of Jacob H. Schiff, Loeb’s son-in-law, it grew to be one of the most influential investment banks in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, financing America’s expanding railways and growth companies, including Western Union and Westinghouse, and thereby becoming the principal rival of J.P. Morgan & Co.
In the years following Schiff’s death in 1920, the firm was led by Otto Kahn and Felix Warburg, men who had already solidified their roles as Schiff’s able successors. However, the firm’s fortunes began to fade following World War II, when it failed to keep pace with a rapidly changing investment banking industry, in which Kuhn, Loeb’s old-world, genteel ways, did not seem to fit; the days of the gentleman-banker had passed.
The firm lost its independence from the Bulge Bracket in 1977 when it merged with Lehman Brothers, creating Lehman Brothers, Kuhn, Loeb Inc. The combined firm was itself acquired in 1984 by American Express, forming Shearson Lehman/American Express and with that, the Kuhn, Loeb name was retired.
History
Kuhn, Loeb & Co. was an investment bank located in New York City. It was founded in 1867, by Abraham Kuhn and Solomon Loeb. Kuhn and Loeb had created a successful merchandising business in Cincinnati, Ohio, when they decided to move east, to New York, to take advantage of the country’s burgeoning economic expansion. Company records indicate that by the time Kuhn and Loeb established their partnership, they were able to capitalize it at $500,000 (equivalent of about $9.7 million in 2021). On January 1, 1875, Jacob Schiff (1847–1920), Solomon Loeb’s son-in-law, joined the firm. He eventually became its leader and grew the firm into the second most prestigious investment bank in the United States behind J. Pierpont Morgan’s J.P. Morgan & Co.
….

It also acted as the leading investment house for John D. Rockefeller, through the guidance of his investment adviser, Frederick T. Gates. Rockefeller invested in many syndicates with the bank, including major stakes in the prominent railroad companies, as well as contributing to its consolidation of the Chicago meatpackers, which resulted in the formation of a leading trust. Overseas ventures that Rockefeller also got involved with included the bank’s loans to the Chinese and Imperial Japanese governments.
The firm also joined a partnership with Rockefeller in 1911 to gain control of the Equitable Trust Company, which was later to merge and become the Chase Bank.[2]
Famous partners of the firm included Otto Kahn, Paul Warburg, Felix Warburg, Mortimer Schiff, Benjamin Buttenwieser, Abraham Wolff, Lewis Strauss, and Sigmund Warburg, founder of S.G. Warburg.
In its early years, intermarriage among the German-Jewish elite was common. Consequently, the partners of Kuhn, Loeb were closely related by blood and marriage to the partners of J & W Seligman, Speyer & Co., Goldman, Sachs & Co., Lehman Brothers and other prominent German-Jewish firms. Prior to the Second World War, a particularly close relationship existed between the partners of Kuhn, Loeb and M. M. Warburg & Co. of Hamburg, Germany, through Paul and Felix, who were Kuhn, Loeb partners. Later on, following World War II, their cousin Sigmund Warburg would briefly continue this relationship as a partner and Executive Director of the firm…
Although the Kuhn, Loeb name is probably gone forever, the firm’s legacy is not. Former Kuhn, Loeb employees remain in senior positions throughout Wall Street, and until recently, at Lehman Brothers. Vestiges of the firm survived in the form of Lehman Brothers’ extensive fixed income capabilities, including many of their bond indices, such as the Government/Credit index. This index, originally created in 1973 by Kuhn, Loeb, as the Government/Corporate index, was among the first generation of bond index data to measure the fixed income market. It is still the preeminent benchmark in its class.
Longest Serving Partners: Jacob H. Schiff (45 years), Felix M. Warburg (40 years)
Clients of the Firm
- American Smelting and Refining Company
- Anheuser-Busch Incorporated
- Automatic Data Processing, Inc.
- Bank Leumi Le-Israel B.M.
- Bayer Foreign Investments Limited
- Bethlehem Steel Corporation
- C.I.T. Financial Corporation
- Chemical Bank New York Trust Company
- Dreyfus Corporation
- Eastern Air Lines, Inc.
- Endicott Johnson Corporation
- Erie Lackawanna Railroad Corporation
- European Coal and Steel Community (forerunner of the E.U.)
- Ford Foundation
- Great Atlantic & Pacific Tea Company, Inc.
- International Telephone and Telegraph Corporation
- Israel Discount Bank Limited
- Kingdom of Denmark
- Kingdom of Norway
- L.M. Ericsson Telephone Company, Sweden
- Metromedia, Inc.
- Metropolis of Tokyo, Japan
- Power Authority of the State of New York
- R.K.O. General, Inc.
- Republic Industrial Corporation
- Republic of Austria
- Republic of Finland
- Republic of Peru
- Republic of the Philippines
- Republic of Venezuela
- Reynolds Metals Company
- Rockwell Manufacturing Company
- Rockwell-Standard Corp.
- Southern Pacific Company
- Stouffer Foods Corporation
- Uniroyal, Inc.
- Mexico (United Mexican States)
- Wagner Electric Corporation
- Western Union Telegraph Company
- Westinghouse Electric Corporation
And the Warburgs report to…
Then came Purim. Firstly we baked Homentashen, filled with poppy seed, with raisins, with plums. We went to Shule `to kill’ Haman. The children used their `Gregers'(# noisemakers) when they heard his `holy’name. In the morning we sent `Sholekh Mones’. On two trays were arranged all sorts of good things, covered with a white cloth. The children took firstly to Grandfather and Grandmother. Father and mother had sent `Sholokh Mones’. Grandmother took off the trays what the children had brought and put all sorts of her good things. And Grandfather gave a few koppecks. We felt so rich, like Rothschild. We went home happy.
THE MEMOIRS OF ROKHEL LUBAN
Rokhel Luban was born in 1898 in the Jewish agricultural colony called Trudoliubovka (also known to the Jews as Engels) in the government of Yekaterinoslav in the southeastern Ukraine.

Ukraine stats
- The latest population estimate for Ukraine is 42,800,000.
- As of 1 January 2016, the core Jewish population of Ukrainians was estimated to be 56,000 (0.13% of the wider population) and the enlarged Jewish population was estimated at 140,000.
- An estimated 200,000 Ukrainians qualify for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return.
- The largest Jewish population centres in Ukraine are Kiev, Dnepropetrovsk, Kharkov and Odessa.
The paragraph below is from Introduction to the Study of the Jewish Agricultural Colonies in the Ukraine by Chaim Freedman, written in 2005. Since then, under the lead of Sylvia Walowitz, Jewish Gen has added a large digital database Courland-Kherson Jewish Relocation 1837-1840 (lists searchable in Latvia and Ukraine databases on Jewish Gen http://www.jewishgen.org).
“In the late 18th century large areas of territories in south-east Ukraine came under the control of the Russian Tsarist regime. At that time this area was known as Novorussia (New Russia) and was divided roughly into three Guberniyas (provinces): Kherson, Yekaterinoslav and Tavritch (the latter included the Crimean peninsula and part of the adjacent mainland). The Russian government was anxious to develop this region by settlement from the rest of the Russian Empire. At the same time the government sought a way to relieve itself of the so-called “Jewish Question”, particularly in what are now Lithuania, Latvia and Belarus. With the accession of Tsar Alexander the First, legislation was passed to define and partially relieve the situation of the Jews. One objective of this legislation was to encourage Jews to leave the crowded and economically poor centers in the north and establish new settlements in Novorussia. Those Jews who qualified to be included in this enterprise were promised financial support to set up agricultural colonies, with the added incentive of exemption from military service (the period of exemption changed at various times throughout the 19th century).”
Russian Jewish agricultural colonies became models for communal agricultural efforts worldwide. Karl Marx cited the kolonii as examples of workers taking control and lifting themselves up through hard work. Zionists in the early 20th century used Russian kolonii as models for Kibbutzim in Israel, particularly in the Second Aliyah after 1904. After the Russian Revolution of 1917, the Bolshevik government carried out collectivization efforts during 1920–1938, see Komzet and OZET. Many kolonii became kolkhozes during this period.
Wikipedia
A more detailed but very brushed history of the colonies is available in the Jewish Encyclopedia.
See also
- Jewish Colonization Association
- Jewish agricultural colonies of Bessarabia
- Jewish gauchos
- The Jewish Steppe
- Kibbutz
- Kolonja Izaaka
- Am Olam
List of Jewish Agricultural Colonies

SOURCE
Ekaterinoslav (Dnyepopetrovsk) Gubernia
- Alexandrovsk (Zaporozhe)
- Andreyevka
- Bakkers (Zatishe)
- Bogodarovka (Novodarovka, Kovilevsk)
- Donetsk (Yuzovka, Stalino)
- Gaichul (Hichur, Novoukrainka)
- Gorykaya (Nazarevitch)
- Gottland
- Grafskoy (Prolotarsky)
- Grunau
- Gulaipole
- Karla Leibnekta
- Khlebodarovka (Suntsove)
- Krasnoselka (Driternumer)
- Ludvigstahl
- Marienfeld (Marinopol)
- Marionovka
- Mariupol
- Mezheritch (Ferternumer)
- Nadeshnaya (Der Vilner)
- Nechayevka ( Gorki, Peness)
- Melitopol
- Mikhailovka
- NovoZlatopol (Pervernumer)
- Orekhov
- Priyutnaya (Takni)
- Reichenfeld (Shirokoye)
- Roskoshnoye (Galushkes)
- Rovnopol (Lates)
- Rozovka
- Sladkovodnaya (Kobilnye)
- Tokmak
- Trudoliubovka (Engels)
- Tsarakonstantinovka (Kubishevo, Kamenka)
- Vasilkovka
- Velikomikhaylovka
- Veselaya (Hoopolova)
- Zaparozhe (Aleksandrovsk)
- Zatishye (Bakhers)
- Zelenopole (Myadler)
- Dribovka
Kherson Gubernia
- Berislaw
- Bolshoi Nagartav
- Bolshoi Sedeimenukha
- Bobovri Kut
- Dibrovka
- Dobraya
- Efingar
- Inguletz
- Israelovka
- Izluchistoye
- Lvovo
- Malaya Nagaratav
- Malaya Sedeimenukha
- Novo Berislav
- Novo Poldol’skiy
- Novopoltavka
- Novo Vitebsk
- Lvovo
- Romanovka
- Volnaya
Tavrida Gubernia
- Berdyansk

Jewish Colonies
- Jewish Gen Kehilalinks webpage for Novopoltavka run by Sylvia Walowitz with contributions from other descendants, many from Argentinian families
- Wikipedia article on the Jewish Agricutural Colonies in the Russian Empire
- Information on Kherson Colonies drawn from The Jewish Encyclopedia Funk and Wagnals 1951
- Colonies of Ukraine on Jewish Gen
- Courland-Kherson Jewish Relocation 1837-1840 lists searchable in Latvia and Ukraine databases on Jewish Gen (www.jewishgen.org)
- Trotsky: A Biography, by Robert Service. Chapter 1, pages 13 – 29
Now let’s do a little Jewish Ukraine Travel:

Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv has had a Jewish population since its founding, and Jewish laborers were involved in its construction. Aside from construction work, many merchants came to the city in order to build businesses selling to the Navy and its sailors. However, Jews were banned from Mykolaiv from 1829-1859, during the reign of the arch-conservative Emperor Nicholas I.
Mykolaiv’s most famous son is Menachem Mendel Schneerson (1902-1994), probably the most important religious figure in 20th century Judaism. His family moved to Yekaterinoslav (Dnipro) in 1907 when his father became the city’s Rabbi. As an adult, he studied in Berlin before the Nazis took power, then went to Paris, where he stayed until the Nazis followed him there as well. The Rebbe escaped to New York on the very eve of the Nazi conquest of Paris. In 1950, he succeeded his father in law to become the seventh leader of Chabad-Lubavitch.
The Rebbe was most influential through his innovations in the field of Kiruv, or outreach. Chabad Houses are found all over the world, and their members are a frequent site handing out shabbat candles and helping men wrap tefilin. Their website is a fantastic resource for Jewish learning as well. Chabad emissaries were sent to Ukraine after the fall of the Soviet Union in order to rebuild Jewish life and most synagogues in the country are Chabad-affiliated. His enormous personal magnetism allowed him to build relationships both across the spectrum of Jewish observance and into the non-Jewish world.

Another famous Jew, though one with a more spotted reputation, who passed through Mykolaiv was Leon Trotsky. Trotsky moved to Mykolaiv as a young adult and began his career as a revolutionary organizing other workers here in 1896. He would later go on to lead the Bolshevik Red Army during the Civil War and was a favored candidate to succeed Lenin, but lost the power struggle to Joseph Stalin. He would then go into exile in Mexico before Stalin had him assassinated.
KHERSON
Located at the mouth of the Dnipro River, the most important trade and transport artery in Ukraine, Kherson was originally envisioned as the heart of the Russian Empire’s expansion on the Black Sea Coast. So much so that it is the final resting place of Grigory Potemkin, the Prince who oversaw the conquest and colonization of the region. However, the Dnipro estuary proved to be too shallow to be as useful of a port, so the city became eclipsed by neighboring Mykolaiv and Odessa.

Ed. note: The colony Vol’naya is not specified on a map because of its isolated position. This colony was located north west of Odessa.
SOURCE
Jews settled in Kherson as soon as the city was founded, and soon made up a large percentage of the city’s merchants. Lumber and grain export were the largest businesses. Outside of the city itself, Kherson region hosted several Jewish agricultural colonies.
The main synagogue of the city, located at Teatralna Street 27, was originally constructed in 1895, but was burned down during the Nazi occupation. After renovating the building, the Soviet authorities turned it into a dormitory for workers at the Petrovsky factory, then later a ward for treating alcoholics. It was handed back to the Jewish community after Ukrainian independence in 1991. It is now renovated and fully operational, with a school and several community organizations.

Kherson oblast is the second least densely populated in Ukraine, and is home to many sites for nature tourism. These include Oleshky Sands, the largest desert in Europe, Askania Nova Nature Preserve, Dzharylhak National Nature Park, and the Dead Sea-like salt pools surrounding Lake Syvash.
MELITOPOL
Melitopol is a moderately sized city in the south of Zaporizhia Oblast that has some of the oldest archaeological finds in Ukraine. The Kamyana Mohyla site, in the outlying village of Myrne, was a religious site from the Neolitic era up through the Medieval period. Before the Russian conquest, the city was a fortified town of the Nogai Turks called Kyzyl-Yar. As the Russian Empire took over the lands of the Crimean Khanate, it became a small village occupied by Cossack families.
In 1842, Melitopol was given its status as a city along with its name, which is Greek for Honey City. Melitopol is still famous for producing honey, as well as cherries. By the late 19th century, it was roughly 40% Jewish. While nearly all of Melitopol’s Jews were killed in the Holocaust and the city is now predominantly ethnic Ukrainian and Russian, they are proud of their diverse roots and are a participant in the Council of Europe’s Intercultural City Program.
Melitopol Synagogue is located on Interkulturna Street, in between Chernyshevs’koho and Mykhaila Hrushevskoho. There is also a memorial to Holocaust victims and the Righteous Among Nations. The statue is, in part dedicated to Vera and her Alla Zemtseva, who rescued Zhanna Tsyparska from the fascists.
THE CROWN JEWEL – ODESSA
Although a settlement existed on the site in ancient times, the history of the modern city began in the 14th century when the Tatar fortress of Khadzhibey was established there; it later passed to Lithuania-Poland and in 1480 to Turkey. The fortress was stormed by the Russians in 1789 and the territory ceded to Russia in 1792. A new fortress was built in 1792–93, and in 1794 a naval base and commercial quay were added. In 1795 the new port was named Odesa for the ancient Greek colony of Odessos, the site of which was believed to be in the vicinity.
Encyclopedia Britannica
Tatars are a Turkic nomadic population related to Khazars, and the two could’ve been easily mistaken one for another by ancient historians.
This stream of immigration carried Jews in large numbers into the city. Eventually this would give Odessa one of the largest concentrations of urban Jews to be found anywhere in the world. During the period from 1815 to 1861, the Jewish population rose from under four thousand to well over seventeen thousand individuals. In 1854, seven thousand Jews were citizens of Odessa, while six thousand other Jewish residents were officially considered to belong to other Russian towns. An English traveler observed: “The Jews form the largest portion of the foreign population. … A few are very rich and engage in the banking business; many make large purchases of imported goods from the foreign merchants and sell them retail in their own shops.
Patricia Herlihy, “Odessa: A History 1794-1914”. Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts
…
Not only did Odessa offer Jews unprecedented economic opportunities and freedom to pursue their own cultural interests, but its liberal atmosphere allowed them some participation in political affairs—a rare prerogative in tsarist Russia. In the 1850s, eleven Jews served in city offices. Both Vorontsov and his successor Stroganov insisted that Jews participate fully in all aspects of the city’s life. This steady influx linked the urban population through familial and other networks with the Jewish settlements in the hinterland. This laid the basis for still more massive immigration after 1861. ”
ODESSA ACCORDING TO Cultural Guide to European Jewry – JGuideEurope
Established in 1794, Odessa was captured by Admiral de Ribas from the Turks for Empress Catherine II of Russia. The city developed rapidly during the nineteenth century, largely due to the arrival of colonists from “New Russia”. It soon became a melting pot of Russians, French, Armenians, Poles, Greeks, Moldavians, and Jews. Forbidden to reside in Saint Petersburg, Moscow or Kiev, Jews poured into the southern Russian cities of Odessa and Nikolayev, eventually constituting a third of their population before the Second World War. Even today, Odessa still bears their mark.
A Jewish city
An Odessan was asked one day,
-How many people live in Odessa?
-One million.
-And how many of them are Jews?
-I just told you. One million.
You see, in people’s minds, “Odessan” and “Jews” are often confused.
Jewish Odessa began at the Greek Square (“Gretsk, that’s what they call the street where the Jews do business”, Sholem Aleichem wrote), Alexandrovski Prospect, the old marketplace, and the streets named Evreiskya, Bazamaya, and Malaya-Arnautskaya. It continued on the other side of Preobrajenska Street, down Tiraspolskaya to Staroportofrankovskaya streets, and beyond that to the neighborhood by the train station. It covered the entire Moldavanka suburb, where the famous Privoz market is found, and ended at the Slobodka district, where the deportation convoys waited during the German-Romanian occupation. The Jewish quarter encompassed a tremendous area, in other words, stretching from downtown all the way to the western and northern suburbs. Before the war, 350000 Jews lived here. They number no more than 50000 today.
Odessa, between yesterday and today
Today, only 3% of Odessa’s population is Jewish, approximately 30000 people. However, the city is still seen as one of Europe’s Jewish capitals. When, in 1916, Isaac Babel, wrote about a “city built by Jews”, he didn’t only refer to the number of Jews, but also to the general atmosphere, tolerant toward minorities.
Recently, archaeologists unveiled Jewish tombs dating from 1770, thus proving that a Jewish community existed there before Odessa’s creation. Indeed, in the 18th century, Jews were salt dealers in this province, that was then known under the name Hadjibey. According to the records, before its conquest by Iossif Derbos, about 10 Jews lived in this region. A hundred year later, there were 138000. The first Jewish inhabitants of Odessa came from the Russian Empire’s shtetls, and from the well-known city of Brody in Galicia. A lots of Jews bore the name of the shtetl they originated from.
The first Jewish inhabitants of Odessa were attracted by the privileges offered by the Russian Empire to the volunteers willing to settle in South Russia. For the Jewish community, it meant escaping the oppression they suffered from in the rest of the Empire. In Odessa, Jews were almost equal to other citizens. Therefore, 100 years after its creation, one third of Odessa’s population was Jewish, and became known as “the star of exile”, as Babel described the zionist movement in the city. Let’s add that leaving the shtetl for Odessa meant -in general- an increased quality of life. For some, the possibility of emigrating to Palestine, from a dream, became a reality. The frequent pogroms also fostered the rise of zionism in Odessa. Still, in 1941, half of the population was Jewish.
Life in the different quarters of the city
To the difference of many cities in the Russian Empire, Odessa didn’t have a Jewish quarter. Although some locations such as Moldavanka, Yevreyskaya, Bazarnaya, and Malaya Arnautskaya were at the center of the everyday community life. Being from small communities, the Jewish population tended to reproduce in Odessa the structural system they knew in the shtetl. Everyday life evolved around the synagogue, the mikveh, the school, the kosher butchery and charitable organizations. The first community newspaper was published in 1795.
The community elite was personified by Brodsky’s Jews, seen as the most educated, wealthy and liberals. In general, the European aspiration of the Brodsky Jews, the fact that Odessa was geographically far away from the centers of Judaism, the diversity if nationalities and social classes composing the city : all those elements explain why Odessa’s community was unique.
At the beginning of the 20th century, Odessa became the biggest market for exchanges and buisinesses in South Russia. Jews managed 90% of the seed export business ; owned 50% of the factories ; produced the white stones that served to the city’s construction ; the Korelsky family managed the biggest tobacco factory of the Empire etc…On the other side, one third of the city’s Jews lived in poverty.
The “Gate to Zion”
Historian Steven Zipperstein notes that the history of Odessa’s Jewish community is closer to the one of San Francisco than the one of Kiev. In this port city, the Jews lived without the constraints and limitations of the Russian Empire. They were not isolated and were an active part of the city’s life. The language barrier didn’t apply as well. However, at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century, the tolerant and multicultural Odessa was nicknamed “Gate to Zion”. Indeed, it became one of the centers of the zionist movement, and the city where thousands of Jews left to Palestine.
The center of the zionist activity was the “Palestine Committee”. This organization helped the relocation of farm workers and craftsmen in Palestine. The committee was initiated in the 1880s by Lev Pinsker, Ahad Haam, Bialik, Klauzner, or Ben Ami were also part of the board. The members also raised funds to buy lands in Palestine. The land were the Hebraic University of Jerusalem was built was purchased by the committee. This is why Lev Pinsker was displaced there in 1934.
One of the most active members of this committee, Meir Dizengoff, was the first mayor of Tel Aviv. This is merely a coincidence. In some respect, Tel Aviv was built in Odessa. Lilienblum, one the yishuv first journalist, wrote that in Odessa, Jews arrived to the shores of the black sea, built a city and developed a port. If they were able to to that in Odessa, they would achieve their goal on the shores of the Mediterranean as well.
Another center of the zionist activity was the Brodsky synagogue. Around 70 houses were built through fund raising executed by the synagogue. Those buildings were the first of the future city of Nes Ziona.
To properly prepare the future emigrants, an Hebrew-only school was opened in 1903. In the same time, the publishing house Moria published school books in Hebrew and sends them to Tel Aviv.
From 1919 to 1927, the boat Ruslan shipped a numerous part of the Odessa intelligentsia to Palestine. Among them, lots were about to become the leaders of the future Israel.
The State Archives of Odessa Region (SAOF) is one of the largest archives in Southern Ukraine. Document holdings include more than 13,100 fonds (record groups) consisting of more than 2,009,604 files. These documents date back to the end of the eighteenth century until the present and reflect the history of the City of Odessa, Odessa Region and Southern Ukraine (formerly Novorussia). A large number of these documents are concerned with Jewish history.
The State Archives of Odessa Region was founded in 1920 as the Odessa Historical Archives. Its main function was the collection of archival documents in the territory of Odessa and Odessa Guberniya (Province), control under departmental archives, responsibility for the safety of valuable materials and the researching and publication of documents. Many famous scientists, public leaders and officials took part in the establishment of the state archival system in Odessa Region.
SAOR began with 22 fonds and collections from various organizations, agencies, religious institutions that concluded their activities after the revolution.
The main fonds of the pre-revolutionary period were:
| • Administration of Novorussia and Bessarabia Governor-General • Odessa City Chief • Odessa City Council • Guardianship Committee for Foreign Settlers in Southern Russia • Odessa Police Office • Commercial Court • Banks • Odessa Port Offices and Customs • Novorussijsky University, colleges and schools • Building organizations • Cultural Societies |
Jewish materials were represented as separate parts of those finds (Jewish sections) or in common management records.
From the mid 1920s until 1940, the Odessa Archive received 33 fonds from Jewish institutions, including:
| • Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society for the Spreading of Learning Among the Jews in Russia • Private Banks of Ashkenazi and Barbash • Odessa City Rabbi |
| • Talmud Torah • College for Artisans of Society “Trud” (Labor”), KOMZET, ORTVERBAND • Odessa Pedagogical Jewish College |
These fonds were of great interest to researchers. During this time, there was open support and acceptance of various ethnic groups. In 1931, the Jewish section in the Odessa Archives was established; the Search Room opened in 1927 and scientists received extensive access to documents. The first Odessa historians working with Jewish records were:
| • S. Borovoj (“Jewish Colonies in Novorussia, 1830-1840”) • L. Strizhak (“Economic state of the Jews in the Steppe Ukraine”) • A. Buzhevich (Jewish Commissions, 1882”) • D. Rishman (“History of Jews in Novorussia”) • A. Reminik (“Jewish Theatre” |
The academician, M. Slabchenko, prepared the materials of Zhaporozje Sich Kosh for publication and located Jewish records among them; but the research and qualified description of them was made by the a young scientist, Saul Borovoj. In 1940, S., Borovoj defended a doctoral dissertation on the subject of “Studying the History of Jews in Ukraine, XVI-XVIII centuries.”
With the beginning of World War II and German-Romanian occupation of Odessa in 1941, a major portion of the documents were evacuated to Stalingrad and later to the town of Uralsk in the West Kazakhstan Region. In Odessa, the City Chief Alexianu ordered the liquidation of “all Soviet garbage” and to convert the archives into a horse stable. The Director of the Archives, G. Serbsky, did not obey and valuable documents were salvaged. Replacements and evacuations led to irrecoverable waste; more than one million files (50% were lost during the war. Jewish fonds also suffered very much. For example, documents destroyed included great portions of materials of:
| • Odessa City Rabbi (320-819 files) • Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society of the Spread of Learning Amount the Jews in Russia (462-495 files) • Odessa House of Jewish • Culture (82-84 files, and others |
In April 1944, SAOR renewed its work in Odessa. After the war, there were not significant incoming Jewish materials other than some private fonds. Since 1990, SAOR has begun the process of declassifying about 900 fonds of German-Romanian Occupying Administrative and other Institutions. These files contain information about the creation of 139 concentration camps and ghettos in”Transnistra,” names of the imprisoned Jews and the policy of genocide.
In 1992, SAOR included records of the former Archives of Odessa Regional Committee of the Communist Party of the USSR (more than 6,000 fonds), including Jewish fonds such as:
| • Odessa Region and City Committees of Poalei-Zion • Odessa Region Committee of Jewish Communist Union of Youth • Editorial Office of the newspaper “Kommunistische Stimme” and others. |
From 1945 until the early 1990s, scientists did not conduct special research on Jewish history. In spite of the fact that Jewish fonds were not secret, there was not any information about them in the Guide to Odessa Archives published in 1961.
Interest in this subject developed from the beginning of the 1990s. During the last 13 years, fifteen foreign researchers, representing scientific center in Germany, Israel, USA, Canada and Japan as well as Ukrainian historians and others have made great contributions to Jewish history using extensive archival sources.
The historical focus on national minorities in Novorussia is one of the main directions of activity in the Odessa Archives in recent years. Materials on Jewish history were presented at some exhibits at the Odessa Historical and Literary Museums. In 2000, the complete register of fonds and collections, including Jewish ones, for pre-revolution period was published, Also, some databases were created including:
| • Name Indexes of the Odessa Jews on Materials of the First All-Russian Census in 1897 (not complete) • Odessa Board for Small Businesses, 1894-1918 |
The name and thematic catalogs of Jews were also brought up to date. SAOR participates in the international program “Documents on History and Culture of Jews in Archives of Ukraine” (Ukraine-Russia-USA).
One of the recent projects of the Odessa Archives is an archeographical edition of Jews of Odessa and Southern Ukraine: History in Documents (End of XVIII-Beginning of XX Century). The book was prepared with support from the Odessa department of the “Joint” and was published in 2003. The book includes:
| 1 | Survey of 72 basic fonds of the Odessa Archives for pre-revolutionary and Soviet periods which contain documents on Jewish history (33 fonds of Jewish institutions, 24 fonds of administrative, court, statistics, customs and other institutions that were related to the subject and 15 private fonds). Description of every fond provides information about inclusive dates and quantity of files, varieties and contents of documents in general. | |
| 2 | Documental Digest. 250 documents on pre-revolutionary history of Jews are represented on 12 thematical lines including: |
| • Legislation on Jews, State policy and the Jewish subject in the Russian Empire • Settlement in Novorussia, Jewish colonies, migration and emigration • Trade, industry, banks • Educational movements; science • Religious and moral life • Charity • Medical institutions and societies • Publishing business • Jewish pogroms • Army service • Participation in revolution movements • Criminal world Document examples • Regulation for Jews (April 13, 1835) • Directions of Higher Authorities about the foundation of the Commission for Education of Jews (1842) • Abolition of kahals (1844) • Settlement of Jews on State lands (1847) • Prohibition of special Jewish clothes (1851) • Visits to police office on day off (1852) • Election order for Jews (1857) • Registration Rules for Jews – foreign subjects (1880) • Materials of the Commission on the Jewish Problem (1881) • Directions regarding admission of Jews to universities (1913) • Circular of the Ministry of Jewish Affairs regarding election to Jewish public boards (1818) • Information about resettling Jews from Podolia to Kherson Guberniyas and the number of Jewish colonies (1835-1839) • Project of some merchants from Kremenchug, Pavlograd and Uman to establish a model Jewish colony of Michailsdorf in Bessarabia (1840) • Report of the Governor-General M.S. Vorontsov regarding reformation of the Jews in Russia (1844) • Appointment of the Mennonite Quenzer to the post of Chief in the colony of Gromokleva (1857) • Conflict and fighting between the Jews and Gypsies in Rezina (Bessarabia) • Activities of the Odessa Society for Relief to Jews, Peasants and Artisans in Syria and Palestine (1888) • Jewish Colonization Society (1892) • Emigration from Odessa to Argentina (1895) • Inclusion of Jews to the Odessa merchants and petty bourgeois • Foundation of A. Rafalovich’s firm (1850) • Society for Bilateral Aid to Jewish counterman (manager) (1862) • Registration of owners of manufacturing enterprises in Odessa (1898) • Information about activities of the M. Ashkenazi firm (1898) • S. Barbash’s bank (1915) • Materials about the Foundation of the Jewish College for Boys in Odessa (1826) • Odessa Jewish Society “Beseda” (Converse”) (1863) • Society for Bilaterial Aid to the Jewish teachers in Novorussia (1866) • Activities of the Talmud Tora in Odessa (1877) • Statistical information about Jewish students in the Novorussijsky University (1881) • Establishing of S. Gurovich and R. Khari scholarships at Odessa Commercial College (1888, 1892) • Activities of the Society “Trud” (1895-1901) • Odessa Affiliate of the Committee of Society of the Spread of Learning among Jews in Russia (1897) • Cheders in Ekaterinoslav and Tavrich Provinces (1903) • Building of the Second Talmud Torah in Odessa (1904) • Activities of Societies of “Ivrija” (1907) • Lovers of Jewish Language (1907) • Club “The Jewish Public Meeting” (1908) • Odessa Jewish Public Nachman Byalik Library “Seifer” (1919) • The College “Yeshivot” (1915-1916) • Documents about the number of synagogues and houses of prayer in Odessa (1840) • Commendation to the Rabbi of the colonies of Novo-Vitebsk, Novo- Podolsk and Novo-Kovno – Rabbi Benjamin Knyazhik with gold medal for good service (1862) • Registration of 63 synagogues and houses of prayer in Odessa with dates of foundation and addresses (1890-1894) • Materials about parishioners of the Brodsky Synagogue (1892-1894) • Statute of the Odessa Society for Jews Converted to the (Russian) Orthodox Faith (1894 • Birth entry of David Oustrach (1908) • Information about the Jewish Hospital in Odessa (1832,1854) • Establishing of the Iosif Valtuch Orthopedic Institute (1888) • Klara Weinberg’s Medical Center for Vaccination against smallpox (1893) • Documents about prohibition of the merchant Aksenfeld to open a printing house in Odessa (1852) • Program of the first magazine for Jews in Russian “Rassvet” (*1860) • Information about edition of “Hamelitz (1867) • “Kadima” (1906) • “Unser Leben” (1912) • “Jewish Anecdotes” (1916 • Materials from the editorial collection of Sergey Stern • Materials about the establishment of: • Odessa Jewish Charity Society (1866) • Kogan’s House (1873) • Jewish Hospice (1880) • Benefections of A. Brodsky, R. Khari, OKhais, M. Morgulis, M. Rabinovich, Rafalovich, Katzen, Luisa Ashkenazi and others for Jewish orphans (1866-1898) • Activities of the Societies of “Druzhelyubije” [“Friendship”] (1898) • Central Jewish Registration Bureau • Reports and notes of the extraordinary Odessa Governor-General, gubernial authorities and Odessa City Chief about pogroms in Odessa and Novorussia in 1881, 1886, 1905 • Evidence from witnesses including Rosa Drutman’s statement about the murder of the Veitzman family in 1905. • Information about the liberation of Jewish students from military service (1844) • Drafting of Jewish peasants who were avoiding military service (1847) • Materials about legal proceedings charging E. Kenis with abetting Jews in avoiding military service (1885-1888). • Materials from the police court case of David Bronstein (Lev Trotsky) arrested for revolutionary activities in Nikolayev (1898) • Reports of police officers about participation of Jews in revolutionary developments, court materials accusing M. Bogomolny with having illegal Bund and Poalei-Zion literature (1904) • Activities of the Jewish Self-Defense guard in Moldavanka [Odessa] (1906) • Relationship of cadets (political party) to the “Jewish Problem” (1908) • Reports of Police and Customs authorities about the Jews engaged in contraband, forgery, prostitution (international), discreditable practices with securities, etc. |
| 3 | Genealogical Chapter, Fond 359: Odessa Board for Small Business, Jewish Section, 1894-1918 (alphabetical name index of 4,505 heads of Jewish families that had a status of Odessa Meshchanin (petty bourgeois) with address locations. |
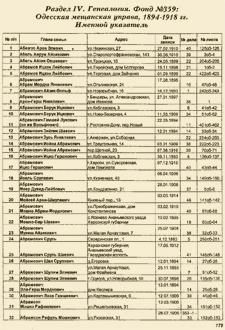 | Page 179 from the above book with an alphabetical name index of 4,505 heads of Jewish families. Information includes name, address, date of birth, age and list number. [Enlarge image] |
Genealogical research is a way to examine the facts through the history of families and to determine the place of an individual in society and his influence on the world. This is an important research focus in order to understand the historical period, its affect on individual families and our place in history.
For example, family history research for the Odessa petty bourgeois Krakhmalnikovs revealed an engrossing story of the development of confectionary production that began in 1892 as a factory and trade firm “The Krakhmalnikov Brothers” and continues to operate now as the Joint Stock Company “Odessa.” By the way, descendants of this family now live in the USA after emigrating from Odessa in 1906. Some family members continue in this occupational field including Bruce Kreig, a grandson of Abram Krakhmalnikov. While he is a professor of Archeology at Chicago University, at the same time he is a famous international expert in food and cooking. After searching the documentary materials in the Odessa Archives, he wrote “We are very happy to know that we are a part of the history of Odessa.”
| The Public Archive of Odessa region Survey of funds and documents HISTORY OF THE JEWS OF ODESSA And SOUTH OF THE UKRAINE “the Jews of Odessa and south of the Ukraine: history in the documents “ (The first volume – end OF THE XVIII – THE XX centuries) SOURCE ADMINISTRATIVE ESTABLISHMENTS Control of the Novorossisk and Bessarabian governor general Office of the Odessa mayor Trustee committee about the foreign settlers of the southern edge of Russia Odessa urban on the compulsory military service presence ESTABLISHMENTS OF THE URBAN And CLASS SELF-GUIDANCE Odessa urban thought, the Odessa urban setting Odessa petty-bourgeois setting POLICE, JUDICIAL, PROSECUTOR And NOTARIAL ESTABLISHMENTS Odessa municipal magistracy Office of the Odessa police chief Elder notary of the Odessa circuit court Odessa merchant’s court |
| FINANCIAL ESTABLISHMENTS And THE JARS Banker house Of Ashkenazi in Odessa ESTABLISHMENTS OF THE RELIGIOUS CULT Odessa municipal ravvinat Cultural-educational SOCIETIES Committee of the Odessa department of the society of the propagation of education among the Jews THE EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS Funds for the higher educational institutions of g.Odessy, general education secondary schools, schools and schools and oranov of their control Odessa Jewish School “Of Talmud- Thor” Odessa 6- Class School Of efrussi FUNDS FOR THE SOVIET PERIOD Funds for the establishments of the period of the temporary German- Rumanian occupation ADMINISTRATIVE ESTABLISHMENTS Control of the Novorossisk and Bessarabian governor general f. 1, 1797-1874, 29624 matters General- governor archive both by the volume and on the significance, is placed in the category of the separately valuable funds GAOO. Since 1803 Odessa was the administrative center of Novorossisk edge and the residence of governor general, who accomplished control of the enormous territory of the Kherson, Ekaterinoslav, Tavricheskeye provinces and Bessarabian region. In the archive of governor is concentrated the information on the history of Jews in the south of the Ukraine v on the different aspects. Legislative acts are widely represented, the resolutions of imperious organs – emperor edicts about the rules of the settling of Jews in by Novorossisk edge, positions about Jews 1835, 1844, position about the box collection of 1839, rules about the production by the Jews of crafts only in the small cities, the settlements and the places (op.2ya8 (1847), d.eeeya). Was preserved the matter for particular office concerning the report of the governor general of the graph Of m.S.Vorontsova to emperor “relative to the assumed measures to the conversion of Jewish people in Russia” (1843, f.y, op.yshche, d.y28). There are opinions and decisions of the chiefs of provinces, information about their fulfillment on the following questions: on the settling of Jews on the particular, landowner’s and fiscal earth (1847-1859 yr, op.2ya9, d.”‘; 1849, op.y92, d.e0; 1854, op.y9e, dd.88-89); on the moving out of Jews to 50 versts from the border of Austria and Prussia (1852, op.2yshch, d.ey); on the limitation of Jews in the trade – opinion of the chiefs of provinces about the equation in the rights of Jews with the Christians (1857, op.y9shch, d.shchya9); on the department of Jews into the special blocks (1856, op.20e, d.ya”); on the prohibition by them entrance into Moldavia (1861, op.y”e, d.2ya); on the order of the selections of Jews to the urban and public posts (1857, op.y9shch, d.”0″); on the subordination of Jews to general control and the destruction of kagalov (1844, op.yshchya, d.e”; 1845, op.y92, d.90); on the establishment of commissions for the formation of Jews (op.y92 (1842), of d.e9); on permission to buy to Jews the earth in the Crimea; on the assignment to the Jew- farmers of the 50- summer privilege of release from the rekrutskoy duty, about the isolation of loans to the acquisition of economy, about the establishment in the Ekaterinoslav province of the colonies of “Israeli Christians”, about the candle and box collections (pub. 248 (1858), dd.2yaye, 2415; op.2ya8 (1843), d.y0shch), the device of hospitals and almshouses (op.2ya8 (1843), of d.y09; op.y9e (1854), d.yy8; op.2ya8 (1854), d.2′”0; op.y”(1868), d.y2y). Was preserved the information about a quantity of kagalov, synagogues and Jewish schools in the edge (op.2yya (1834, d.e), about the collection of donations to the construction of synagogues and of houses of prayer (1842, op.2ya8, d.9’), about the establishment in Odessa of Jewish school (op.y90 (1826 g.) d.ya”) and handicraft classes in by Novorossisk edge (op.y9e (1853), d.98). A number of documents they reflect the process of Jewish colonization. These are materials about land surveying of the earth for the device of colonies, application of the Jews of Podolskiy, Grodnenskoy and Vitebskoy of provinces about the migration into the Kherson province (1837, op.yya8, d.y; 1838, d.shch; 1840, d.ee, 2728); the information about the desire of merchants to found model Jewish colony in Bessarabia (1840, op.2yshch, d.y’). There are permissions of authorities to the delivery of passports for the entrance from abroad or of migration from other provinces of Russia, information about the state of Jewish colonies (1841, op.2ya8, d.2″Рё; 1843, op.2ya8, d.y08, 115), about the Jew- farmers (1859, op.y’, d.y0shch), about the measures for an improvement in control of the Jewish settlings (1843, op.2ya8, d.yy0), about the “disorders” in the colonies (1841, op.2ya8, d.89). Materials on the colonization are concentrated in the fund also on the separate inventory – “about the Jewish colonies of Novorossisk provinces” (inventory 2, 1837-1847, 101 matters). This of order and the reports of the central and local administrative bodies of control about the outlet of the earth in the Kherson and Ekaterinoslav provinces for the settling of Jews and device for them of agricultural colonies, the assignment of fiscal means for the building of the houses of colonists, the determination of the staff of officials and supervisors for control of the newly formed settlings. There are petitions of Jews of Podolskiy, Kurlyandskeye, Vitebsk, Mogilev, Grodnensk, Kovenskeye and Minsk provinces about the migration into Novorossiyu, and also applications of some colonists about the permission by it to return in the previous place of residence, about the delivery of passports and tickets for the departure to the earnings. In the documents is contained valuable information about the development of Jewish colonies beaver Kut, greater and small Nagartav, Seydemenukha, Ingulets, Yefengar, Kamenka, tortuous (Khortitskiy district), Izrailevka (Bobrinetskiy district), new Berislav, L’vov, Romanovskoye, Novopoltavka (Kherson district) – statistical evidence, reports and the review of the officials of the department of the state asset and other officials about the development of agriculture and handicraft matter, wine ransom, about a quantity of inhabitants and the status of the health of population, the device of training and medical institutions, in particular, in Nagartave, the passage of some colonists from judaic to orthodox faith, applications of Jews about their reckoning in farmers, about their release from the rekrutskoy duty. Office of the Odessa mayor f. 2, 1802-1837, 1848-1854, 1856-1917, 20890 matters The materials of fund are systematized on 16 inventories, comprised in accordance with the structure of the office: tables capable, secret, economic, construction, certified, societies and meetings, 1 All-Russian population census. Inside each inventory the matters are systematized in the chronological order with some retreats. Materials on the history of Jews do not compose united collection, but they bear the separate nature and they are included in all structural parts. Capable table (inventories 1, 1a, 1b, 4 – ch.2, 1796-1919 yr.) Orders of mayor about the order of compilation of public sentences, about the order of conducting, to checking and zasvidetel’stvovanii of the Jewish metric books, about the establishment of handicraft classes with the fiscal Jewish schools, about the introduction of examination for the teachers of Jews, about the Odessa Jewish hospital. Lists about a quantity of Jews in Odessa, kagalov, synagogues and houses of prayer, information about discovery and activity of synagogues and of houses of prayer, selections of their officials. Information about the Odessa rabbis, in such cases to shvabakhere, doctor of philosophy To krepse. Information about the commercial houses, the enterprises, the drugstores and the therapeutic establishments – Abraham rafalovich, the steamer offices Kossodo, Rappoport et al., particular hospitals Of gurovich, Polukhera, Meringa and the assertion of the regulations of the orthopedic institute of Joseph val’tukh in Odessa. Orders relative to Jewish rites and customs – about the prohibition since 1851 to the Jews of the carrying of special Jewish clothing, about the prohibition to appear into the urban police during subbotniye and authorized days, to arrange wedding festivals on the streets of Odessa, to woman- jewesses to shave heads, to accomplish some religious rites not by rabbis. Matters about the assignment of the right of trade in Russia to Jews -inostrannopoddannym only to the merchants of the 1st guild, about the enumeration of Jews into the agricultural title, about the permission to Jews to open printing houses, in particular, to merchant aksenfel’d. Permissions to the publication of newspapers and periodicals, in such cases. “dawn”, “gamelits”. Information about the collisions between the Jews and the Christians on the religious soil, about the activity of London missionaries for the rotation of Jews into Christianity. Permissions about the erection of Jews into the honorable citizenship – I.Gorovitsa, M.Gurovicha, etc. _ matter about permission found different society – mutual assistance Jewish salesman, “conversation, mutual assistance Jew, mutual assistance jewess, Jewish blagotvoritelСЃogo charity association, society for propagation education between Jew, society for propagation craft between Jewish woman, mutual assistance Jew, assistance farmer and craftsman in Syria and Palestine, society for assistance inverted in Christianity Jew, society care about poor and homeless Jewish child, society mutual aid merchant agent and different merchant- Jew, society sanitary colony for treatment and training weak health study indigent Jewish population Odessa, society assistance require toiler- Jew Odessa, society for benefit former pupil commercial school Fa1ga, society care about poor Jewish population on settlement -Romanovke, society assistance by the student of the commercial school Of gokhmana, society of working aid to the requiring themselves Jews of Odessa, society “friendliness” and other. Materials about the charitable activities – about the donation A.Brodskim of house and 50 thousand rubles for the Jewish orphans and the device of barracks for 30 patients, about the establishment in the Jewish orphan house of allowance to im.Ashkinazi and of other nominal allowances, and also of allowance Of rafalovicha in the Jewish orphan house, the device of house for the aged Jews, the establishment by the Jews of almshouse, the donation Of l.Ashkinazi 76500 rub to the construction of operating building in the Odessa Jewish hospital. Orders concerning the educational institutions, in particular, school “eshibot”, the commercial school of the name Of gurovicha, school “labor”, the musical classes Of plinera, “Talmud- tori”, the dancing classes Of khaimovicha and Krymershmoysa, musical is course Rafalovicha, bandmaster it is course Kauffmann, drawing is course Reynbol’da, to the professional school of the practical painting Of tovelevicha. Materials about the establishment into 1875 with the mayor of the post of scientific Jew and reports of scientific Jews (Genikesa and of others.) Secret table (inventory 2, 1820-1912; op.ye, 1874-1910 yr.) On inventory 2: the matter for search and establishment of supervision after the persons, suspected of the criminal and political crimes, on the delivery of evidence about the loyalty. Lists of political prisoners, materials on the dispatch to the settling into Siberia and other province. Circular about the prohibition of voluntary offerings among the Jews by the name “collection to the Israeli earth”. Documents and the protocols of commission for Jewish problem. Matters about the transfer from Warsaw to Odessa of the monthly Jewish journal “gaboker-Or”, about the assertion of the program of weekly political- public and literary Jewish newspaper in the Russian language “love” edited by Yakov Prilukera. On inventory 13: the matter of office about the Jewish pogroms in Odessa in 1905 (dd.e-shch). Economic table (inventory 3, 1830-1916) Permissions to the discovery of industrial and commercial enterprises, information about the state of factories and plants, commercial houses, application in questions of owner’s activity. Deal about the construction of Odessa Jewish hospital of 1860; on the sums of box and candle collections and the content of Jewish schools 1864 about the discovery of the enterprises: Gamsheyem by Wolf, By b.Rozenbergom – vodka distilleries, by Siegal, by Schechter, by Vaynberg – factories of water and lemonade, Rafalovichem – the plant of starch and of solodovareniya, Gurovichem – the factory of finishing it is pin and the preparation of vinegar, By perel’muterom – cosmetic institution, by Frenkel – the factory of the preparation of fraction, dynamic meter Gusevs, By roytblat, b. by goose, by Barban – cotton factories, Shorshteynom – sheet metal factory, Brodskim – sugar refinery, by Bronstein – the medovarennogo plant, etc; on the assertion of plan for the construction of Jewish cold synagogue. Sudnyy table (inventory 4, 1828-1914 yr.) Materials about sale of the immovable properties for the debts, selection of complaints and claims, spiritual wills and guardianships, penalty of duties, expulsion of an alien abroad on the charge in the criminal and political crimes, performance of judicial sentences, into t.ch.:ob abduction by foreign Jews abroad of the russkopoddannykh women for the completion in Konstantinopole of public houses (d.”, 2483); on the delivery to the Jews of metric evidence; “about the investigation of denunciation about the formed gang of Jews, which issues the false of passport to the departure abroad. 1882 g.”,” on the complaint of the parishioners of Odessa main synagogue of improper actions of the warden of the synagogue Of a.Kupervassera on the post “; the alphabets of prisoners; rule for the activity in Russia of joint-stock Jewish colonization company and information about its work 7670); “about the meetings of Zionist- Jews”. Construction committee (inventory 5, 1812-1901 yr.) Information about the construction of public buildings, the outlet of the urban earth to private individuals, the activity of urban architects, in particular, about the service in the post of the architect of the 5th part of Odessa not the class artist of Joseph kolovich (drafter Of brodskoy synagogue). Certified table (inventory 6, 1808-1912 yr.) Passport, tickets to the entrance into Russia or the departure beyond its limits for the years 1808-1898 (they were preserved not completely). Matters to the individual citizens on the reckoning in Odessa petty bourgeois merchants, on the drive to the oath and the delivery of evidence to those, who accepted Russian citizenship, to the delivery of foreign passports, in particular, to avstriyskopoddannomu rabbi gersh To dannemarku in the passage into S- Petersburg, Moscow and Kiev. Lists about the foreigners, who arrived from abroad. Table of societies and meetings (inventory 7, 1906-1914 yr.) There are permissions to the establishment, the regulations and the information about the activity of societies and meetings of g.Odessy. Are introduced the society of the mutual aid of those been of handicraft society “labor”, the society of assistance to Jew- farmers and craftsmen in Syria and Palestine, Odessa territorialistskoye emigratory society, the union of Jewish charity associations and establishments “central Jewish registration bureau”, the department of Vilenskiy of the charitable Jewish society Of “gmilus-Khesed”, the society of the amateurs of Jewish language, Jewish public meeting in Odessa, the Jewish society Of “ivriya”, and also different professional societies with the traditionally high percentage of the participation of Jewish population – particular agents, brokers, photographers, industrialists, etc. First All-Russian population census of 1897 (inventory 8, 9, 10) The sheets of census with 3 thousand addresses were preserved, in them were registered the surname, name and patronymic of inhabitant, his age and the place of generation, citizenship, class, formation, religion, social position, profession, sources of income. (in 1897 the number of Odessa residents, who showed by native language Jewish, was 124511 man. – 2-4 on the number national group after Russians). Trustee committee about the foreign settlers of the southern edge of Russia f. 6, 1800-1873, 14815 matters In the fund for 9 inventories, in the inventories в„–в„– 1a, 3 and 4 there are divisions on the Jewish table, in the rest the materials according to the Jews are not isolated as separate complexes. In the fund were put off the materials on the colonization of Novorossisk edge, in such cases about the appearance and development of Jewish colonies in the Ekaterinoslav and Kherson provinces. These are reports and the list of the supervisors of Jewish colonies, circumferential orders and shul’tsev about the population, the welfare of colonies (statistical evidence since 1811), the penalty of taxes, the delivery of loans, the elections of officers, the development of agriculture, horticulture, trade; the application of the Jews of the western provinces of the Russian Empire about the migration into the newly formed colonies, about their reckoning in colonists and other classes, about the Jewish schools, about the fight with the vagabondage of Jew- colonists. Interest they can represent materials about the realization of government plan with respect to the involvement of Jews in productive zemledel’chestvo on the model of the well organized German farmer economies, the reciprocal effect of Jewish and mennonitskikh colonies – for example, about the building by mennonitami of houses for the arrived Jews in the colony To nechayevke, about the designation of wardens from mennonitov into the Jewish settlings, in particular, David Hertz into the colony to L’vov, about the migration of mennonitov in a constant place of residence into the Jewish colonies for the purpose of the development of there particular production, about the creation of the mixed settlings (Yudenplan in Khortitse), about the isolation by mariupol’skimi mennonitami of wheat for the sowing to Jew- colonists, about the orders by the Jews of agricultural instruments and seeds in molochanskikh mennonitov, etc. Odessa urban on the compulsory military service presence f. 315, 1884-1920, 1022 matters Materials according to the Jews are not isolated as separate complex. Lists of reservists and their metric vypisi (beginning from 1884 of generation), the private affairs of draftees, correspondence on the postponements of military service. ESTABLISHMENTS OF THE URBAN And CLASS SELF-GUIDANCE Odessa urban thought, the Odessa urban setting ff. 4, 16, 1796-1920, 67818 matters The Duma and setting knew by economic, financial, construction and businesses. Jewish department: f. 4, inventory 107 (1824-1872, 1034 matters) f. 4, inventory 108 (1884-1895, 120 matters) f. 16, inventory 109 (1896-1903, 76 matters) f. 16, inventory 110 (1904-1912, 183 matters) f. 16, inventory 124, part of 2, p. 399-423 (1870-1920 yr.) Annual reports of Jewish department. Information about the start of the arrived in Odessa Jews in petty-bourgeois and merchant class, the transfer from the class into the class, the restoration in the class and the exception from the same. Family and personal lists of Odessa Jew- petty bourgeois, merchants and craftsmen. Lists of Jews musical spark gaps and shops. Metric books and the lists of the borne and dead Jews (men), not registered in Odessa municipal ravvinate, in particular, by that belonging not to what konfessii. Correspondence on the certification of metric evidence about the generation, marriage, death and to the correction of errors in metric records. The decisions of setting about the establishment of the events of the generation of those, who do not be registered according to the metric books, and the alphabetical lists of such citizens. Correspondence on the delivery of passports, it is specific to the residence, evidence and other documents. Tax lists of Odessa petty-bourgeois Jewish class. Correspondence and lists on the rekrutskim collections, on the apportionment of candle and box collections. Lists of Jewish schools and materials about their content, in particular, the report of the member of the setting N.A. Of gantsa about the delivery in 1919 to the Jewish community of subsidy in the amount of 3806000 rub to the content of 28 elementary schools. Lists of Jews, which entered educational institutions. Information about building and discovery of synagogues and houses of prayer. Lists of synagogues and houses of prayer and their terms. Information about the officials of Jewish society – rabbis To fil’shteyne, Stopchike, Polinkovskom, To shvabakhere, the wardens of synagogues Abraham -Xasime, To kupervassere, scientific Jew Solomon To guroviche, etc. Materials about the donations, the content disabled, charitable actions, allocation of assets to the content of Jewish hospital, Jewish cemeteries, shelters. Lists of philanthropists and their spiritual wills (A.M.Brodskogo, etc.). Besides the inventories on the Jewish department, funds for 4 and 16 contain additional those 144 comprised on the years of inventory – on the general office management, the construction and charitable departments, the public education and the bookkeeping, in which also there is an information on the history of Jewish community against the background of townspeople life. The significant interest present the yearly lists of merchants, who declared capital, to list about the collection of taxes, materials about the discovery of commodity-industry enterprises, the outlet of the sections of the urban earth under the individual building, the participation of citizens in the urban self-guidance. The comparative analysis of documents can give idea about the formation, the increase and the motion of the private capital, formation and development of Jewish commercial houses, economic state of both the Jewish community as a whole and its individual representatives. In the fund for setting was preserved “the periodical of the honorable citizens of Odessa. 1854-1897 “, into which were carried 304 surnames of distinguished and most authoritative in the Odessa society citizens, in such cases of 96 Jews and karaites with the members of their families. Odessa petty-bourgeois setting f.eshch9, 1828-1919, 200 matters Jewish department (1894-1918, 44 matters) is represented by the family lists of the Odessa petty bourgeois- Jews (list it contains the names of all members of family with the indication of their age or date of generation, relation to the military service, the addresses of stay at the moment of the composition of document over the signature of the head of family). POLICE, JUDICIAL, PROSECUTOR And NOTARIAL ESTABLISHMENTS Odessa municipal magistracy f. 17, 1795-1839, 162 matters Magistracy knew by the administrative and judicial matters of Odessa petty bourgeoisie and merchants. In its office management were put off the most important and chronologically earliest materials of economic nature – the information about the delivery of commercial and estimated evidence, about the assertion of merchant women, zaprodazhnykh, borrowed letters, introductions into the estate, about the selection of commercial transactions, bankruptcies, complaints. There are also lists, lists and correspondence about a quantity of merchants and petty bourgeois, their properties and capital, organization it is shop particular applications about the reckoning into the Odessa merchants and the petty bourgeoisie, in particular, for the years 1808-1809. – M.Sh.Medyanika, Levi and Aron pibergod, Solomon and Abel Gershkovichey, Leyby of Krakow, tsesarskopoddannogo T.G.Kumana, etc. (op.e), Leyby Of balabana, Abraham bondoni, Gilelya Of manusovicha, Mordko Of moshkovicha, Mendel Doyberga, Yakuba Lando, Getselya Of fridentalya, Moshi Mangubi, etc. (op.shch), the information about the individual citizens, in such cases Jews, added into the Odessa petty bourgeoisie in 1811-1812. Documents about the erection of Jews in the post or the suspension from it are of interest also. In the fund there is an “alphabet about the Jews” in 1811 (op.e, d.yayashch) Office of the Odessa police chief f. 314, 1824-1917, 437 matters Fund contains reports, reports, correspondence of the officials of the police about search and detention of the persons, suspected and accused in the criminal and political crimes; the lists of citizens, which consist under the supervision of the police, the political prisoners of Odessa prison, exiled to the hard labor works, the members of underground organizations, participants in the revolutionary movement, Jewish pogroms in Odessa. There is information about the participation of Jews in the revolutionary movement. The political matters can serve as an example: on the participation in the preparation of attempt on governor in 1902 of the members of the party of the terrorists, in number of whom of 30 pupils of school “labor”; on the creation in 1907 by young Jews headed by leftist Mochmanom – by the workers of the plant of gene – guard by the name “young will” in contrast the “union of Russian people” and their participation in the “expropriation” of private property; on the witnesses on business Of beylisa; on the establishment By i.A.Trivusom, Ya.Landesmanom, S.Rabinovichem and By i.B.Smirom of “Odessa Zionist club KADIMA”; on the activity of “Jewish territorialisticheskoy organization” and its theorist Israel To zangvile; on supervision after the sect of subbotniks and “zhidovstvuyushchikh” and others. Fund is rich in the materials, which tell about the role of Jews in the criminal peace. From the criminal cases present interest materials about the activity in Odessa of the criminal groups of fal’shivomonetnogo and gambling business, sutenerstva, smuggling, and also of information about the well-known criminals – international pocket pilferer To moyshe To miroshnike-Irline (Bear- American), the international souteneurs Isaac Goldstein and the silverer, the cardsharper Zinof golender in the nickname “Pushkin” et al. Elder notary of the Odessa circuit court f. 35, 1869-1920, 32404 matters Funds contain the notarial reports about the buying and selling, the donation, the will of the immovable property and land sections, given to the estates, agreements about the transactions, concluded by the notaries of g.Odessy, the Odessa, Anan’evskogo and Tiraspol’ districts of Kherson province. There is, for example, information about the enterprises Of frola Of shpolyanskogo. Odessa merchant’s court f. 18, 1808-1920, 5072 matters Materials on the selection of commercial transactions, the delivery of estimated evidence, the collection of the commercial duties, matter for guardianship, commercial insolvency, registration of commercial institutions in the territory of Odessa mayorship. There are books of the registration of commercial establishments (1836-1843), of list about the property and capital of merchants (1826-1843), investigation and judicial matters for bankruptcies, promissory note actions, containing valuable information about activity and state of Jewish commercial houses. FINANCIAL ESTABLISHMENTS And THE JARS Banker house Of Ashkenazi in Odessa f. 246, 1893-1918, 5 matters Materials on establishment and activity of the joint-stock company of southeastern steam navigation “star” of the banker house Of ashkenazi. Balances and reports on the operation of steamship “eastern star” (1906-1916). Statements about the income, which is subject to taxation by the state income tax (1917-1918). ESTABLISHMENTS OF THE RELIGIOUS CULT Odessa municipal ravvinat f. 39, 1846, 1854, 1875-1920, 499 matters The metric books about the generation, the marriage, divorce and death of the Jews Odessa and alphabets to them – base source for the genealogical studies (documents of ravvinata for the years 1835-1874 they perished in the years of 2-1 world war). The funds for another konfessiy – Kherson spiritual consistory (f. 37), Evangelical- Lutheran and reform arrivals (ff. 630, 894) – contain information about the passage of Jews from judaic religion to Christian, about the marriages of israelites with the representatives of other religions, about the registration of Jews, who belong not to what faith. Cultural-educational SOCIETIES Committee of the Odessa department of the society of the propagation of education among the Jews f. 442, 1880-1881, 36 matters Regulations of the Odessa department of society, correspondence on organizational questions also about its activity. Protocols of the general meetings of the members of society; the application of students about the rendering by them of material aid, the determination to the pedagogical work; correspondence with the Petersburg committee, particular Jewish and other educational institutions for questions of the organization of enlightenment work among the Jews, delivery of means to the content of educational institutions, job placement of teachers, method of donations. Lists of instructors, members of society; the information about the Jewish schools of g.Odessy, the libraries of department and their reports. Brief survey of the activity of Odessa department, estimate of libraries and museum. Information about the members of the society THE EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTIONS Funds for the higher educational institutions of g.Odessy, general education secondary schools, schools and schools and oranov of their control (about 40 funds) Tyuey ppozvolyayut to investigate such questions as shaping of intellectual layer in the Jewish medium, level of the education of Jews, their contribution to the cultural and scientific life of city. Thus, in the materials Of rishel’evskogo face (f. 44, 1817-1865, 3262 matters) are considerable valuable information about trained in this Odessa’s first higher educational institution Jews. Created on the base of face in 1865. Novorossisk university (f. 45, 1865-1920, 44688 matters), only in the south of the Ukraine, played large role in the making of a Jewish intelligentsia Of novorossii. In kon.KhyKh- of nach.KhKh of substances the Jews composed significant layer among the students of Odessa. The private affairs of students – remarkable historical source, which makes possible for researcher to personify epoch. The matter contains, as a rule, application about the method into the educational institution and the release at its end, copy of metric evidence about the generation, the secondary school graduation certificate, information about the behavior and progress, photograph of student. In kon.Kh.IKh – nach.KhKh of substances in by Novorossisk university were trained many representatives of well-known Jewish families. In the fund for Odessa highest female it is course (f.eeya, 1906-1920, 11321 matters) numerous information about the jewess- girl students. Odessa Jewish School “Of Talmud- Thor” f. 441, 1891-1906, 13 matters Correspondence with the Odessa urban setting on organizational and economic questions. Circulars and the order of the inspector of people schools for training- organizational and financial-economic questions. Information about the composition of the trustee council of school, the rules of the internal regulation (d.y0); application about the delivery of benefits being required. List of students. Odessa 6- Class School Of efrussi f. 125, 1898-1901, 714 matters Minutes of the meeting of pedagogical council. General and examination lists about the successes, the behavior, the diligence and the abilities of students. Circular orders of the trustee of Odessa training region about the designation of teachers and their rewarding, about the grant-aided students. Lists of those entering, students and external students. Class, table and object periodicals. Curricula (op.y, d.ya’). the Receipt- cashbox books of payment for the instruction and the income- expense books. Photographic cards of external students (op.y, d.’y; op.2, d.eya), information and the certification of external students (op.2, d.28). The private affairs of students (op.e, 607 matters). FUNDS FOR THE SOVIET PERIOD In the funds for administativnykh control elements 1930- X yr. (councils, their executive committees and the subordinate structures of all levels) – the information about the nationalization of property in well-off citizens, the dekulakization. The materials of the inspectorates of public education (ff. 150, 134, 1919-1930, 2201 matters) tell about the activity of Jewish sections, schools, libraries, the creation in Odessa of the unique museum of Jewish culture. The documents of the independent funds for Jewish public organizations, educational institutions and political parties reflect many aspects of the state national policy of post-revolutionary period with respect to the poorest part of the Jewish population – creation of Jewish national regions, collective farms and agricultural comradeships, the organization of the system of the national educational institutions, cultural societies for the Jews, the activity of international organizations for rendering aid to the victims of pogroms in the period of Civil War in the Ukraine and starving, migration into Birobidzhan, departure of Jews into Palestine, activity of youth associations. Funds for the establishments of the period of the temporary German- Rumanian occupation 887 funds, 1941-1944. The materials of the organs of authority and control, created with German- Rumanian authorities in the temporarily occupied territory of Odessa and Odessa region give idea about the catastrophe of Jewish people in period 2- of world war. The documents of boards, pretur, prefectures, working communities, enterprises and establishments contain information about the creation of the network of concentration camps and ghetto in the newly formed governorship Of transnistrii and concentration in them of Jewish population, about rendering aid concluded Rumanian Jewish communities. There are numerous lists of those, who were being located in the ghetto. By the colleagues of archive is created the alphabetical nominal card index of victims and indicator about the presence of lists on 139 ghetto Of transnistrii (Mogilev, Bershad’, Berezovka, Kameneq- Podolskiy, Obodovka, Domanevka, etc.). Since 1990 archive gave out sv.yshch of thousand of information to citizens about the confirmation of their stay in the ghetto within the framework of the implementation of international programs on the compensation for the substituted to them damage. The demands of these citizens also can be examined as the significant historical source, since the detailed descriptions of tragic events, morale of the prisoners of ghetto, fates of concrete people are contained in many. |
Sources for the Jewish Agricultural Colonies, adjacent towns and villages, located at various times in Southern Ukraine, Bessarabia, Podolia and the Crimea, are relatively hard to find. This site gathers data about the individual settlements, the points of origin of these settlers and recounts their stories.
…AND THEN USSR PUT THE AGRO-JOINT OUT. IS THIS WHAT zELENSKY AND PUTIN ARE WORKING TO REPAIR?

On page 404 we find a mention for:
“Warburg, Edward M. (1908–1992). AJJDC Chairman, 1941–1943, 1946–1965.”
Yeah, I know Russian Bolshevik / communist oligarchy was initially Jewish for the most part, I’ve already discussed it in earlier reports. But that changed over time, as the party became a humongous soviet monster, there simply weren’t enough Jews to provide for all regional leaderships and gentiles eventually established their own “nobility”, even though Jews maintained many top positions. A new hungry generation of commies is like a new wave of locusts. I saw the same process happening in my home-country, Romania.
And from here everything just falls in line like a Russian-made Tetris game.




This is either too big of a coincidence or not a coincidence.
We don’t do coincidence theories around here.

LATER UPDATE: MORE COINCIDENCES
To be continued?
Our work and existence, as media and people, is funded solely by our most generous supporters. But we’re not really covering our costs so far, and we’re in dire needs to upgrade our equipment, especially for video production.
Help SILVIEW.media survive and grow, please donate here, anything helps. Thank you!
! Articles can always be subject of later editing as a way of perfecting them

SEE DETAILS / ORDER














