If you’re familiar with our reports, George Church is no stranger to you either. He’s a founder figure for the Human Genome Project, CRISPR and The BRAIN Initiative. But he’s totally not getting the deserved attention, seeing that he’s just turned our world upside down. Not by himself, of course.


Remember when Fauci and Big Tech joined efforts to keep us in the dark in regards to the mRNA impact on our genetics and DNA?
We’ve shown that there’s an entire new field of science that does just that: argues what Fauci said by using RNA to reprogram DNA. YouTube ad Facebook censored this.
Let’s see how are they going to argue this gentle giant of the science world and all his dark entanglements:
Video deleted, of course, but you can WATCH IT ON ODYSEE
George M. Church biography as per Harvard website
Professor at Harvard & MIT, co-author of 580 papers, 143 patent publications & the book “Regenesis”; developed methods used for the first genome sequence (1994) & million-fold cost reductions since (via fluor-NGS & nanopores), plus barcoding, DNA assembly from chips, genome editing, writing & recoding; co-initiated BRAIN Initiative (2011) & Genome Projects (GP-Read-1984, GP-Write-2016, PGP-2005:world’s open-access personal precision medicine datasets); machine learning for protein engineering, tissue reprogramming, organoids, xeno-transplantation, in situ 3D DNA, RNA, protein imaging.

George Church is Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School and Director of PersonalGenomes.org, which provides the world’s only open-access information on human Genomic, Environmental & Trait data (GET). His 1984 Harvard PhD included the first methods for direct genome sequencing, molecular multiplexing & barcoding. These led to the first genome sequence (pathogen, Helicobacter pylori) in 1994 . His innovations have contributed to nearly all “next generation” DNA sequencing methods and companies (CGI-BGI, Life, Illumina, Nanopore). This plus his lab’s work on chip-DNA-synthesis, gene editing and stem cell engineering resulted in founding additional application-based companies spanning fields of medical diagnostics ( Knome/PierianDx, Alacris, AbVitro/Juno, Genos, Veritas Genetics ) & synthetic biology / therapeutics ( Joule, Gen9, Editas, Egenesis, enEvolv, WarpDrive ). He has also pioneered new privacy, biosafety, ELSI, environmental & biosecurity policies. He is director of an IARPA BRAIN Project and NIH Center for Excellence in Genomic Science. His honors include election to NAS & NAE & Franklin Bower Laureate for Achievement in Science. He has coauthored 537 papers, 156 patent publications & one book (Regenesis).


PhD students from (* = main training programs for our group):
Harvard University: Biophysics* , BBS* , MCB , ChemBio* , SystemsBio* , Virology
MIT: HST*, Chemistry, EE/CS, Physics, Math.
Boston Universty: Bioinformatics, Biomedical Engineering
Cambridge University, UK: Genetics
Publications, CVs-resumes, Lab members , Co-author net, ELSI
Technology transfer & Commercial Scientific Advisory Roles
Personal info — News — Awards — Grant proposals
Director of Research Centers: DOE-Biotechnologies (1987), NIH-CEGS (2004), PGP (2005), Lipper Center for Computational Genetics (1998), Wyss Inst. Synthetic Biology (2009). Other centers: Regenesis Inst. (2017), SIAT Genome Engineering (2019), Space Genetics (2016), WICGR, Broad Inst. (1990), MIT Media Lab (2014)
Updated: 15-Jan-02021

The BRAIN initiative[edit]
He was part of a team of six[80] who, in a 2012 scientific commentary, proposed a Brain Activity Map, later named BRAIN Initiative (Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies).[81] They outlined specific experimental techniques that might be used to achieve what they termed a “functional connectome“, as well as new technologies that will have to be developed in the course of the project,[80] including wireless, minimally invasive methods to detect and manipulate neuronal activity, either utilizing microelectronics or synthetic biology. In one such proposed method, enzymatically produced DNA would serve as a “ticker tape record” of neuronal activity. – Wikipedia

Wyss Institute Will Lead IARPA-Funded Brain Mapping Consortium
January 26, 2016
(BOSTON) — The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University today announced a cross-institutional consortium to map the brain’s neural circuits with unprecedented fidelity. The consortium is made possible by a $21 million contract from the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) and aims to discover the brain’s learning rules and synaptic ‘circuit design’, further helping to advance neurally-derived machine learning algorithms.
The consortium will leverage the Wyss Institute’s FISSEQ (fluorescent in-situ sequencing) method to push forward neuronal connectomics, the science of identifying the neuronal cells that work together to bring about specific brain functions. FISSEQ was developed in 2014 by the Wyss Core Faculty member George Church and colleagues and, unlike traditional sequencing technologies, it provides a method to pinpoint the precise locations of specific RNA molecules in intact tissue. The consortium will harness this FISSEQ capability to accurately trace the complete set of neuronal cells and their connecting processes in intact brain tissue over long distances, which is currently difficult to do with other methods.
Awarded a competitive IARPA MICrONS contract, the consortium will further the overall goals of President Obama’s BRAIN initiative, which aims to improve the understanding of the human mind and uncover new ways to treat neuropathological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, autism and epilepsy. The consortium’s work will fundamentally innovate the technological framework used to decipher the principal circuits neurons use to communicate and fulfill specific brain functions. The learnings can be applied to enhance artificial intelligence in different areas of machine learning such as fraud detection, pattern and image recognition, and self-driving car decision making.
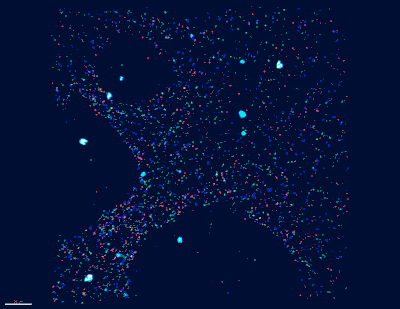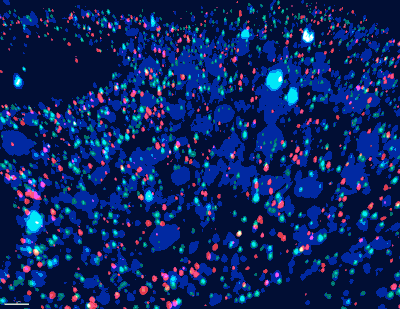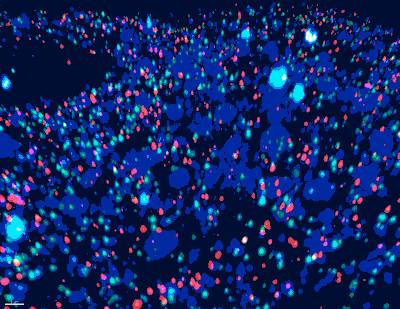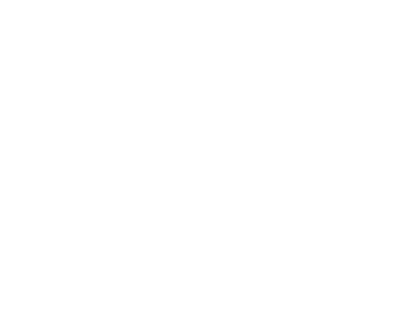
“Historically, the mapping of neuronal paths and circuits in the brain has required brain tissue to be sectioned and visualized by electron microscopy. Complete neurons and circuits are then reconstructed by aligning the individual electron microsope images, this process is costly and inaccurate due to use of only one color (grey),” said Church, who is the Principal Investigator for the IARPA MICrONs consortium. “We are taking an entirely new approach to neuronal connectomics_immensely colorful barcodes_that should overcome this obstacle; and by integrating molecular and physiological information we are looking to render a high-definition map of neuronal circuits dedicated first to specific sensations, and in the future to behaviors and cognitive tasks.”
Church is Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School, and Professor of Health Sciences and Technology at Harvard and MIT.
To map neural connections, the consortium will genetically engineer mice so that each neuron is barcoded throughout its entire structure with a unique RNA sequence, a technique called BOINC (Barcoding of Individual Neuronal Connections) developed by Anthony Zador at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Thus a complete map representing the precise location, shape and connections of all neurons can be generated.
The key to visualizing this complex map will be FISSEQ, which is able to sequence the total complement of barcodes and pinpoint their exact locations using a super-resolution microscope. Importantly, since FISSEQ analysis can be applied to intact brain tissue, the error-prone brain-sectioning procedure that is part of common mapping studies can be avoided and long neuronal processes can be more accurately traced in larger numbers and at a faster pace.
In addition, the scientists will provide the barcoded mice with a sensory stimulus, such as a flash of light, to highlight and glean the circuits corresponding to that stimulus within the much more complex neuronal map. An improved understanding of how neuronal circuits are composed and how they function over longer distances will ultimately allow the team to build new models for machine learning.
The multi-disciplinary consortium spans 6 institutions. In addition to Church, the Wyss Institute’s effort will be led by Samuel Inverso, Ph.D., who is a Staff Software Engineer and Co-investigator of the project. Complementing the Wyss team, are co-Principal Investigators Anthony Zador, Ph.D., Alexei Koulakov, Ph.D., and Jay Lee, Ph.D., at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Adam Marblestone, Ph.D., and Liam Paninski, Ph.D. are co-Investigator at MIT and co-Principal Investigator at Columbia University, respectively. The Harvard-led consortium is partnering with another MICrONS team led by Tai Sing Lee, Ph.D. of Carnegie Mellon University as Principal investigator under a separate multi-million contract, with Sandra Kuhlman, Ph.D. of Carnegie Mellon University and Alan Yuille, Ph.D. of Johns Hopkins University as co-Principal investigators, to develop computational models of the neural circuits and a new generation of machine learning algorithms by studying the behaviors of a large population of neurons in behaving animals, as well as the circuitry of the these neurons revealed by the innovative methods developed by the consortium.
“It is very exciting to see how technology developed at the Wyss Institute is now becoming instrumental in showing how specific brain functions are wired into the neuronal architecture. The methodology implemented by this research can change the trajectory of brain mapping world wide,” said Wyss Institute Founding Director Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D., who is also the Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and the Vascular Biology Program at Boston Children’s Hospital and Professor of Bioengineering at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. – WYSS Institute
IARPA is CIA’s DARPA.
DARPA IS RAN BY PENTAGON AND IARPA BY CIA.
IARPA IS EVEN MORE SECRETIVE, DARING AND SOCIOPATHIC.
Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks (MICrONS)
Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA)
Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies. (BRAIN)
Background
The science behind Obama’s BRAIN project. (BrainFacts, 15Apr-2013 | Jean-François Gariépy)
Wyss Institute Will Lead IARPA-Funded Brain Mapping Consortium (Wyss, 26-Jan-2016 |)
Project Aims to Reverse-engineer Brain Algorithms, Make Computers Learn Like Humans (Scientific Computing, 4-Feb-2016 | Byron Spice)
The U.S. Government Launches a $100-Million “Apollo Project of the Brain” (Scientific American, 8-Mar-2016 | Jordana Cepelewicz)
Grant Proposal
Tasks 2 & 3 PDF Harvard, Wyss, CSHL, MIT.
Task 1. CMU.
 Related Projects:
Related Projects:
Full Rosetta brains in situ
A. Activity (MICrONS = Ca imaging) (Alternative=Tickertape, see figure to right)
B. Behavior (MICrONS & Alt = traditional video)
C. Connectome (MICrONS & Alt = BOINC via Cas9-barcode)
D. Developmental Lineage (via Cas9-barcode)
E. Expression (RNA & Protein via FISSEQ)
Building brain components, circuits and organoids.
Busskamp V, Lewis NE, Guye P, Ng AHM, Shipman S, Byrne SS, Sanjana NE, Li Y, Weiss R, Church GM (2014)
Rapid neurogenesis through transcriptional activation in human stem cells. Molecular Systems Biology MSB 10:760:1-21


Flagship Pioneering’s Scientists Invent a New Category of Genome Engineering Technology: Gene Writing
Tessera Therapeutics emerges from three years of stealth operations to pioneer Gene Writing™ as a new genome engineering technology and category of genetic medicine

NEWS PROVIDED BY Flagship Pioneering
Jul 07, 2020, 08:00 ET
CAMBRIDGE, Mass., July 7, 2020 /PRNewswire/ — Flagship Pioneering today announced the unveiling of Tessera Therapeutics, Inc. a new company with the mission of curing disease by writing in the code of life. Tessera is pioneering Gene Writing™, a new biotechnology that writes therapeutic messages into the genome to treat diseases at their source.
Tessera’s Gene Writing platform is a potentially revolutionary breakthrough for genetic medicine that addresses key limitations of gene therapy and gene editing. Gene Writing technology can alter the genome by efficiently inserting genes and exons (parts of genes), introducing small insertions and deletions, or changing single or multiple DNA base pairs. The technology could enable cures for diseases that arise from errors in the genome, including monogenic disorders. It could also allow precise gene regulation in other diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic diseases.
“While profound advancements in genetic medicine over the last two decades had therapeutic promise for many previously untreatable diseases, the intrinsic properties of existing gene therapy and editing have significant shortcomings that limit their benefits to patients,” says Noubar Afeyan, Ph.D., founder and CEO of Flagship Pioneering and Chairman of Tessera Therapeutics. “Our scientists have invented a new technology, called Gene Writing, that has the ability to write therapeutic messages into the genomes of somatic cells. We created Tessera to pioneer its applications for medicine. However, the breakthrough is broad and could be applied to many different genomes from humans to plants to microorganisms.”
A New Era of Genetic Medicine
Geoffrey von Maltzahn, Ph.D., an MIT-trained biological engineer; Jacob Rubens, Ph.D., an MIT-trained synthetic biologist; and other scientists at Flagship Labs, the enterprise’s innovation foundry, co-founded Tessera in 2018 to create a platform that could design, make, and launch Gene Writing medicines. A General Partner at Flagship Pioneering, von Maltzahn has co-founded numerous biotechnology companies, including Sana Biotechnology, Indigo Agriculture, Kaleido Biosciences, Seres Therapeutics, and Axcella Health.
“DNA codes for life. But sometimes our DNA is written improperly, driving an enormous variety of diseases,” says von Maltzahn, Tessera’s Chief Executive Officer. “We started Tessera Therapeutics with a simple question: ‘What if Nature evolved a better solution than CRISPR for inserting curative therapeutic messages into the genome?’ It turns out that engineered and synthetic mobile genetic elements offer the potential to go beyond the limitations of gene editing technologies and allow Gene Writing. Our outstanding team of scientists is focused on bringing the vast promise of this new technology category to patients.”
Mobile genetic elements, the inspiration for Gene Writing, are evolution’s greatest genomic architect. The first mobile genetic element was discovered by Barbara McClintock, who won the 1983 Nobel Prize for revealing the mobile nature of genes. Mobile genetic elements code for the machinery to move or copy themselves into a new location in the genome, and they have been selected over billions of years to autonomously and efficiently “write” their DNA into new genomic sites. Today, mobile genetic elements are among the most abundant and ubiquitous genes in nature.
Over the past two years, Tessera has been mining genomes to discover novel mobile genetic elements and engineering them to create Gene Writing technology.
Tessera’s Gene Writers write therapeutic messages into the genome using RNA or DNA templates. RNA-based Gene Writing uses an RNA template and Gene Writer protein to either write a new gene into the genome or guide the rewriting of a pre-existing genomic sequence to make a small substitution, insertion, or deletion. DNA-based Gene Writing uses a DNA template to write a new gene into the genome.
By harnessing the biology of mobile genetic elements, Gene Writing holds the potential to overcome the limitations of current genetic medicine approaches by:
- Efficiently writing small and large alterations to the genome of somatic cells with minimal reliance upon host DNA repair pathways, unlike nuclease-based gene editing technologies.
- Permanently adding new DNA to dividing cells, unlike AAV-based gene therapy technologies.
- Writing new DNA sequences into the genome by delivering only RNA.
- Allowing repeated administration of treatments to patients in order to dose genetic medicines to effect, which is not possible with current gene therapies.
Tessera has licensed Flagship Pioneering’s intellectual property estate, which was begun in 2018 with seminal patent filings supporting both RNA and DNA Gene Writing technologies.
Tessera’s Scientific Advisory Board includes Luigi Naldini, David Schaffer, Andrew Scharenberg, Nancy Craig, George Church, Jonathan Weissman, and John Moran, who collectively have decades of experience in developing gene therapies and gene editing technologies, and also have commercial expertise from 4D, UniQure, Casebia, Cellectis, Magenta, and Editas. Tessera’s Board of Directors includes John Mendlein, Flagship Executive Partner and former CEO of multiple companies; Melissa Moore, Chair of Tessera’s Scientific Advisory Board, Chief Scientific Officer of Moderna, member of the National Academy of Sciences, and founding co-director of the RNA Therapeutics Institute; Geoffrey von Maltzahn; and Noubar Afeyan. The 30-person R&D team at Tessera has deep genetic medicine and startup expertise, including alumni from Editas, Intellia, Beam, Casebia, and Moderna.
About Tessera Therapeutics
Tessera Therapeutics is an early-stage life sciences company pioneering Gene Writing™, a new biotechnology designed to offer scientists and doctors the ability to write and rewrite small and large therapeutic messages into the genome, thereby curing diseases at their source. Gene Writing holds the potential to become a new category in genetic medicine, building upon recent breakthroughs in gene therapy and gene editing, while eliminating important limitations in their reach, utilization and efficacy. Tessera Therapeutics was founded by Flagship Pioneering, a life sciences innovation enterprise that conceives, resources, and develops first-in-class category companies to transform human health and sustainability.
About Flagship Pioneering
Flagship Pioneering conceives, creates, resources, and develops first-in-category life sciences companies to transform human health and sustainability. Since its launch in 2000, the firm has applied a unique hypothesis-driven innovation process to originate and foster more than 100 scientific ventures, resulting in over $34 billion in aggregate value. To date, Flagship is backed by more than $4.4 billion of aggregate capital commitments, of which over $1.9 billion has been deployed toward the founding and growth of its pioneering companies alongside more than $10 billion of follow-on investments from other institutions. The current Flagship ecosystem comprises 41 transformative companies, including Axcella Health (NASDAQ: AXLA), Denali Therapeutics (NASDAQ: DNLI), Evelo Biosciences (NASDAQ: EVLO), Foghorn Therapeutics, Indigo Ag, Kaleido Biosciences (NASDAQ: KLDO), Moderna (NASDAQ: MRNA), Rubius Therapeutics (NASDAQ: RUBY), Sana Biotechnology, Seres Therapeutics (NASDAQ: MCRB), and Syros Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ: SYRS). – Flagship Pioneering
To be continued?
Our work and existence, as media and people, is funded solely by our most generous supporters. But we’re not really covering our costs so far, and we’re in dire needs to upgrade our equipment, especially for video production.
Help SILVIEW.media survive and grow, please donate here, anything helps. Thank you!
! Articles can always be subject of later editing as a way of perfecting them


